Description
Abaqus Hydrogen Cracking | Abaqus Hydrogen Damage
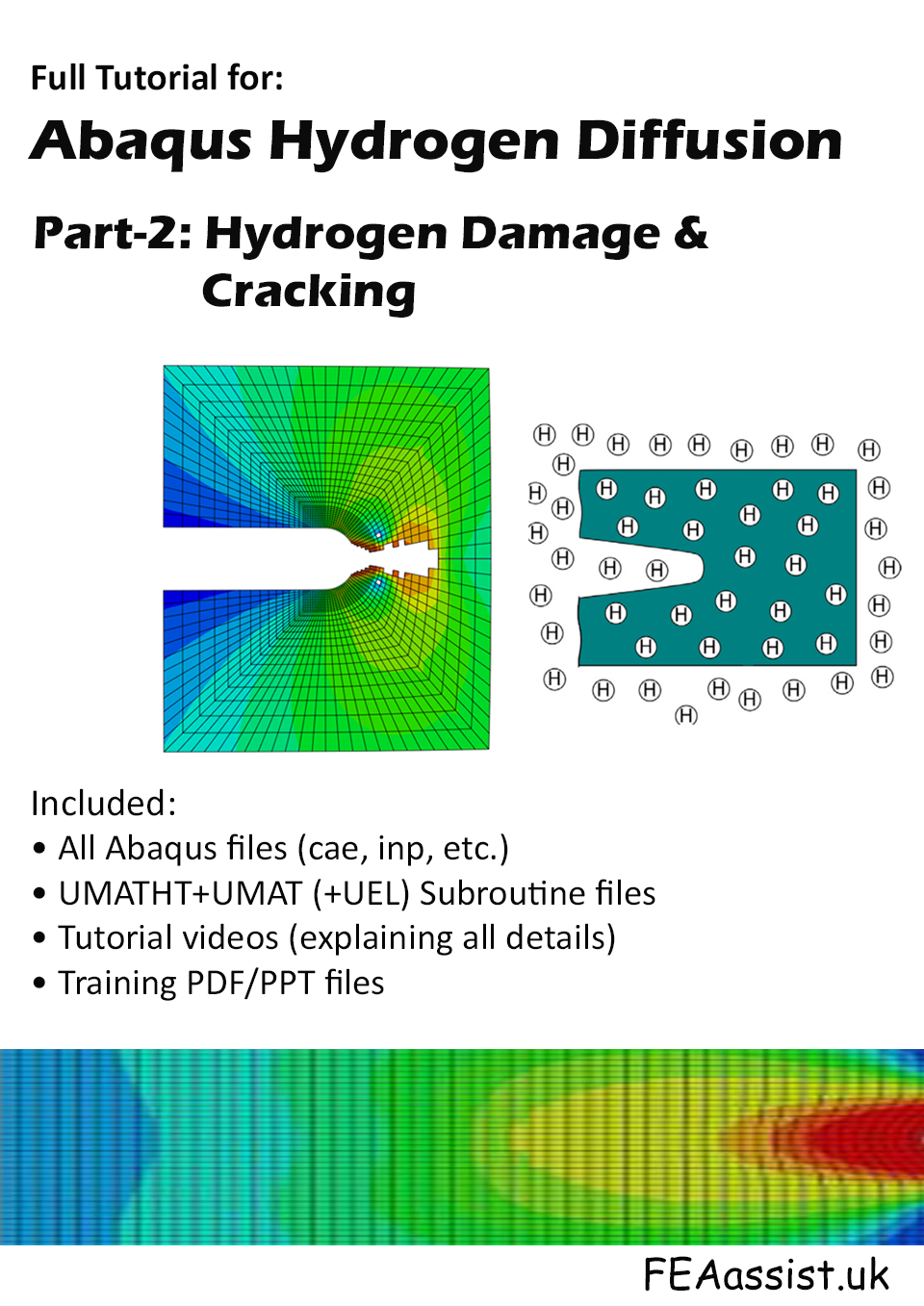
Engineers increasingly require reliable Abaqus hydrogen cracking models capable of predicting hydrogen-dependent strength degradation under complex stress states. This package provides a validated Abaqus hydrogen damage modeling framework based on a stress-controlled fracture criterion derived from peer-reviewed research. The formulation predicts hydrogen embrittlement fraccture simulation behavior by coupling stress invariants with hydrogen concentration, enabling realistic prediction of brittle fracture initiation in hydrogen-charged materials. Unlike phase-field or cohesive approaches, this implementation uses a hydrogen damage UMAT in Abaqus based on a modified Mohr–Coulomb failure surface. The model captures the effect of stress triaxiality, Lode angle, and hydrogen content on fracture stress, allowing accurate simulation of hydrogen-assisted cracking in Abaqus under engineering loading conditions.
The methodology follows the framework published in Engineering Fracture Mechanics (2024) and is fully compatible with Abaqus/Standard developed by Dassault Systèmes [1,2,3,4], ensuring industrial applicability and computational robustness. This is Part-2 of the Abaqus Hydrogen Modeling Suite and builds directly on the diffusion–mechanics coupling developed in Part-1.
What Abaqus Hydrogen Cracking Package Implements
1️⃣ Stress-Based Abaqus Hydrogen Damage Criterion
The cracking formulation is based on a modified Mohr–Coulomb (MC) failure model, expressed in stress invariant space.
The failure stress depends on:
- Stress triaxiality (η)
- Lode angle parameter (θ̄)
- Hydrogen concentration (cₗ)
The fracture stress surface is defined as:
σ̄f(η, θ̄, cₗ) = c₂(cₗ) × f(η, θ̄)
Failure occurs when maximum principal stress reaches the critical MC stress.
This allows hydrogen-dependent brittle fracture prediction in Abaqus.
2️⃣ Linear Damage Accumulation Law
Damage evolves according to:
D = ∫ dσ₁ / σ̄f(η, θ̄, cₗ)
Under proportional loading:
D = σ₁ / σ̄f
Fracture initiates when:
D = 1
This provides:
- Stable stress-controlled failure prediction
- Mesh-objective formulation (with proper refinement)
- Clear physical interpretation of fracture onset
3️⃣ Hydrogen-Dependent Cohesive Strength
As hydrogen concentration increases, fracture stress decreases non-linearly and brittle fracture becomes dominant (implemented in hydrogen damage UMAT Abaqus).
Scientific Background of the Model
This implementation is based on the published work:
Fracture prediction on hydrogen-charged notched samples using a stress-state-dependent phenomenological model
Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2024.
The study:
- Investigated hydrogen-charged AISI 4135 steel
- Used notched tensile specimens
- Calibrated Mohr–Coulomb parameters from experiments
- Validated numerical fracture loads against test data
- Achieved <10% difference between simulation and experiment
The framework:
- Couples plasticity and hydrogen concentration
- Assumes equilibrium hydrogen distribution
- Targets stress-controlled brittle fracture
- Focuses on HEDE mechanism
Pricing Options for Abaqus Hydrogen Cracking
Choose the package that matches your needs. If your project requires hydrogen cracking, hydrogen damage modeling, or full 3D Abaqus hydrogen diffusion, the complete suite is the option.
Choose Your Hydrogen Modeling Capability
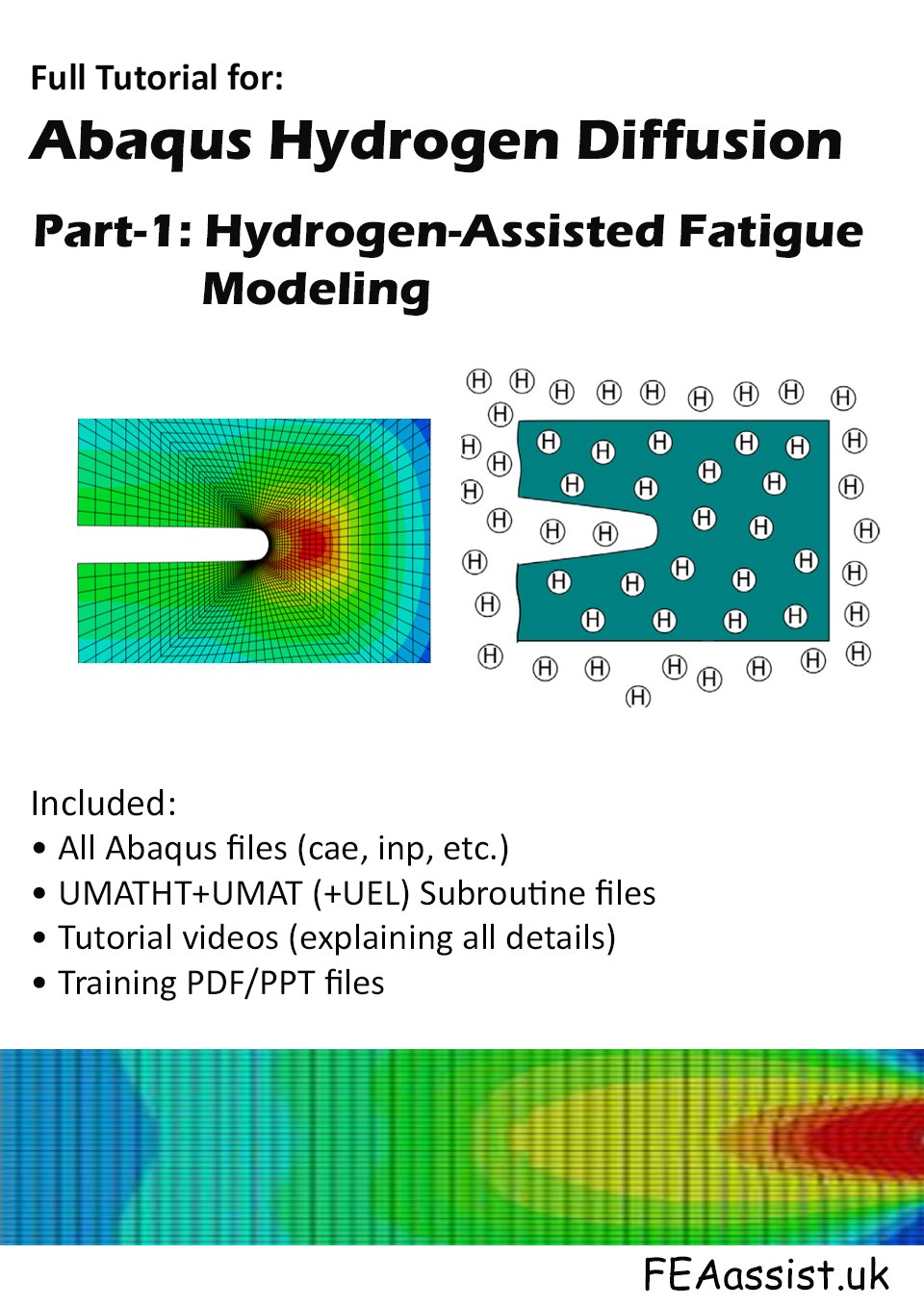
Part 1 — Diffusion–Fatigue
- ⚙️ Stress-assisted diffusion
- 🧲 Multi-trap transport
- 💻 UMAT + UMATHT + UEL
- 📂 Tutorials & files
£199 (Student: £139)
Part 2 — Damage & Cracking
- 🧠 Diffusion–damage coupling
- 🔬 Hydrogen degradation
- 📈 Crack growth modeling
- 🧩 Advanced workflow
£299 (Student: £229)
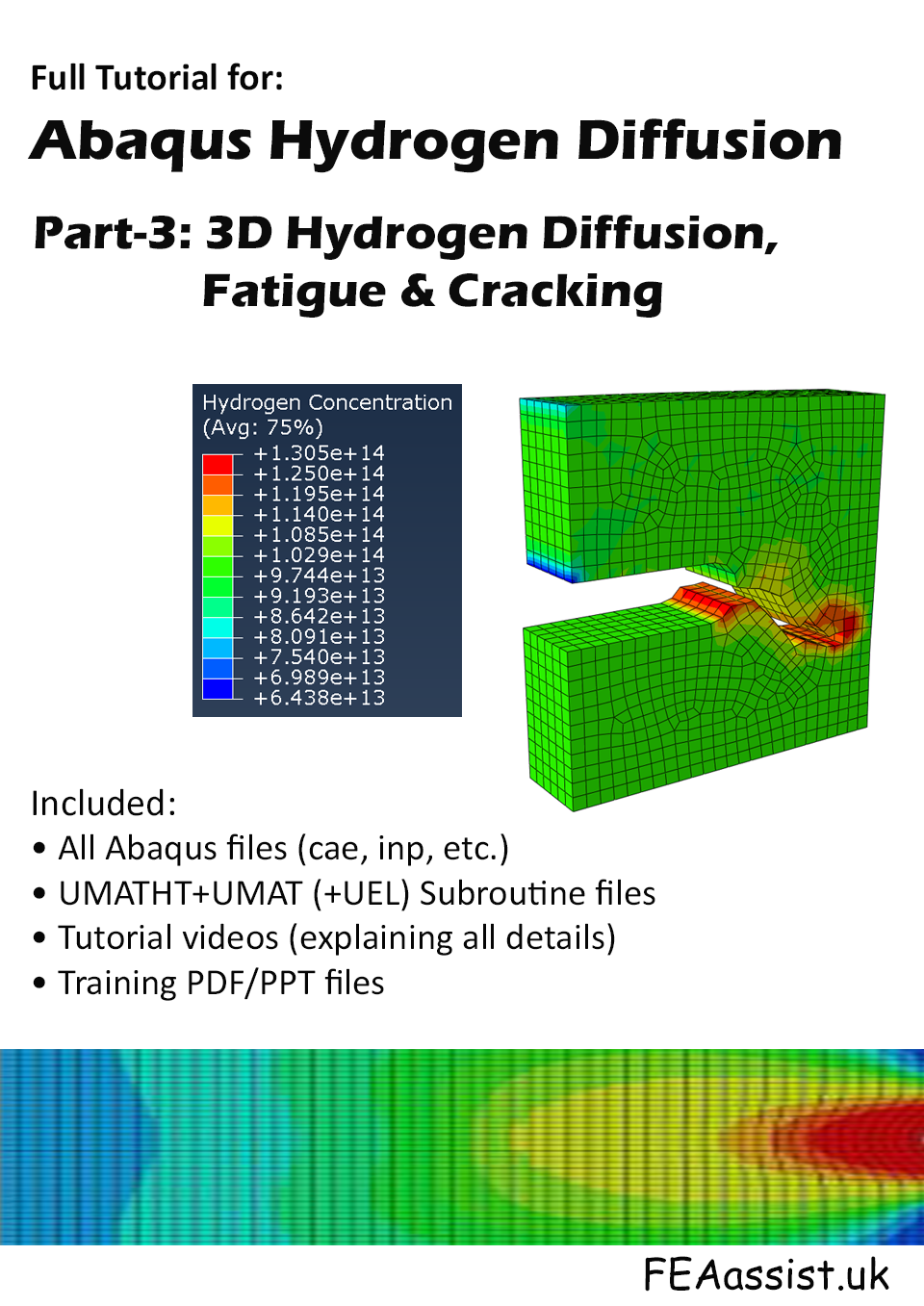
Part 3 — Full 3D Simulation
-
- 🌐 3D diffusion–fatigue–cracking
- 🏗 Real geometries
- 🏭 Industrial modeling
- 📘 Advanced documentation
£399 (Student: £319)
Complete Hydrogen Suite
- ✔ Diffusion & Fatigue modeling
- ✔ Damage & cracking
- ✔ Full 3D simulations
£599 (Student bundle: £449)
Optional Add-Ons & Supports (Abaqus hydrogen damage)
In addition to the core hydrogen cracking package, you can enhance your experience with tailored support and consulting services:
🔎 Consultation Add-On
Personalized Abaqus hydrogen embrittlement modeling support for your project. Choose the duration that fits your needs:
- 2 hours – £199
- 4 hours – £299
- 8 hours – £499
Ideal for bespoke model setup, interpretation assistance or advanced customization.ce.
Upgrade Abaqus hydrogen damage to Hydrogen diffusion or Full 3D Modeling
This product focuses on Hydrogen Diffusion cracking in Abaqus. If you want to simulate hydrogen diffusion, fatigue, or full 3D diffusion-fatigue-cracking,
explore these advanced packages:
- ➡️ Part 1: Abaqus Hydrogen Diffusion and Fatigue
- ➡️ Part 3: 3D Diffusion–Fatigue–Cracking Package
- ➡️ Complete Hydrogen Suite: Best value bundle for all implementations
🚀 Order Project 🔬 Continue to Hydrogen Part-1 & 3
Advanced Crack Modeling?
For variational fracture and phase-field crack propagation methods, see our advanced implementation: Abaqus Phase Field Fracture Package.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.